In modern industrial and commercial facilities, control systems have become a cornerstone of operational efficiency. These systems manage equipment, monitor performance, and provide critical insights that allow operations to run smoothly. With the growing demand for energy efficiency, automation, and sustainability, control systems are evolving to enable data-driven operations, providing unprecedented visibility into facility performance and process optimization.
Traditional control systems relied on basic monitoring and manual adjustments. Operators would manually track metrics, make decisions based on experience, and respond reactively to system issues. While functional, this approach limited the ability to optimize energy use, anticipate maintenance needs, and identify inefficiencies across complex operations. The emergence of modern control systems has transformed this approach by providing continuous data monitoring and intelligent analytics.
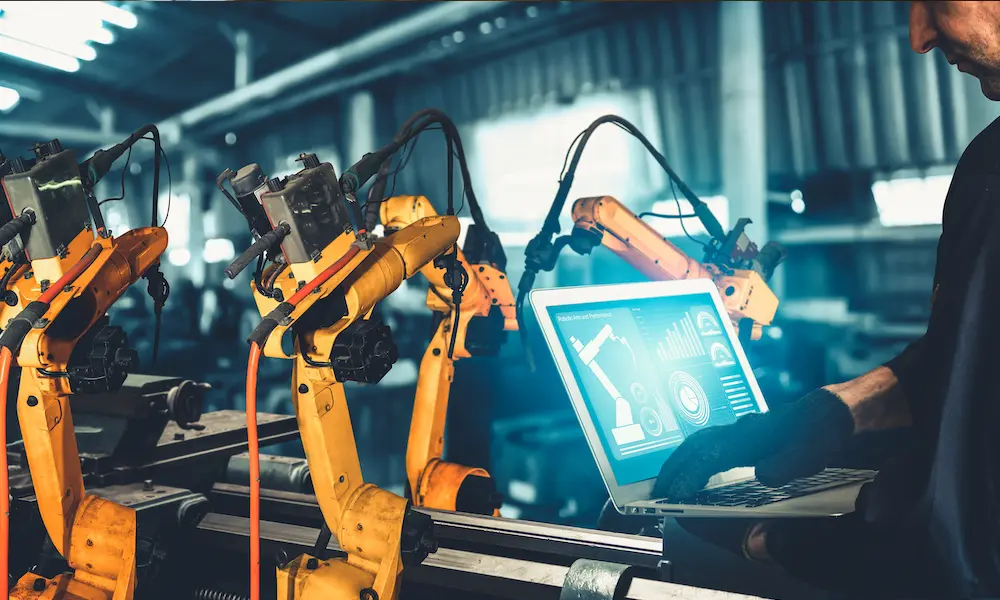
A key component of these systems is the integration of networked devices and sensors that continuously collect operational data. Equipment can now communicate performance metrics in real time, allowing teams to identify patterns and make proactive adjustments. Industrial automation plays a critical role here, enabling processes to be executed consistently while feeding valuable data into the control system. This creates a foundation for data-driven decision-making that improves efficiency, productivity, and reliability.
Even smaller components like the load center are now part of a broader digital ecosystem. Modern load centers can monitor power distribution, track energy usage, and report anomalies that may indicate inefficiencies or potential equipment issues. Incorporating these devices into control systems allows facilities to manage energy consumption more effectively and implement targeted strategies to reduce waste. This integration provides visibility across both the electrical infrastructure and operational processes, supporting a holistic approach to energy management.
Data-driven operations extend far beyond energy monitoring. Modern control systems can analyze operational patterns to predict maintenance needs, optimize equipment schedules, and improve overall facility performance. Predictive maintenance, for instance, reduces unplanned downtime by identifying issues before they lead to equipment failure. This approach not only improves operational reliability but also extends the life of machinery and reduces overall maintenance costs.
Centralized control is another significant benefit. By consolidating monitoring and management into a single platform, operators can oversee multiple systems simultaneously. Real-time dashboards provide a clear view of performance metrics, enabling quicker responses to anomalies and facilitating more informed operational decisions. Centralized control also supports remote management, allowing oversight of multiple facilities or production lines from a single interface.
Energy efficiency and sustainability are directly supported by data-driven control systems. Continuous monitoring allows facilities to detect areas of high consumption, implement demand-based adjustments, and track the effectiveness of energy-saving initiatives. Smart systems can even automate these adjustments, reducing waste and supporting sustainability goals without requiring constant human intervention. Over time, the data collected also helps identify trends and opportunities for process improvement, further enhancing operational performance.
Integration is critical in achieving these benefits. Control systems are most effective when they connect various aspects of a facility, including HVAC systems, lighting, industrial machinery, and power distribution. A unified system allows for coordinated operation, ensuring that processes run efficiently while minimizing energy consumption. This connectivity also enhances safety by providing real-time alerts and automated responses to prevent equipment damage or hazardous situations.
Simplifying data access is another important consideration. Even with advanced monitoring, insights are only valuable if they can be easily understood and acted upon. Modern control systems provide intuitive dashboards, analytics tools, and reporting features that translate complex data into actionable information. Teams can track key performance indicators, compare historical trends, and implement process changes based on reliable insights. This approach empowers facilities to continuously improve operations without overwhelming staff with raw data.
The evolution of control systems also includes predictive analytics and machine learning capabilities. By analyzing historical and real-time data, these systems can identify inefficiencies, forecast energy demand, and suggest operational adjustments. This proactive approach reduces energy waste, improves equipment performance, and supports more informed planning for production and maintenance schedules. Over time, data-driven operations become increasingly optimized, creating a cycle of continuous improvement.
Security and reliability remain essential components of modern control systems. Protecting operational data and ensuring uninterrupted system performance are critical for maintaining efficiency and preventing costly downtime. Modern systems incorporate secure communication protocols, redundancy, and automated alerts to address issues before they impact operations. A robust and secure control system allows facilities to confidently leverage data-driven insights while safeguarding critical processes.
In conclusion, control systems are enabling a shift from reactive management to data-driven operations. By integrating networked sensors, centralized dashboards, and predictive analytics, facilities can optimize energy usage, improve equipment performance, and enhance operational efficiency. Even devices such as load centers contribute to this ecosystem, providing visibility and control over energy distribution. Modern control systems support proactive decision-making, sustainability initiatives, and continuous process improvement, making them essential tools for facilities looking to operate at peak efficiency in today’s industrial landscape.